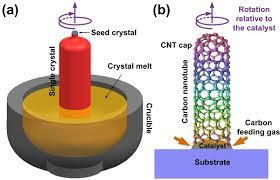
Methods to prepare a large single crystals of metals has two main ways :
1- Solidification from the melt .
2- Grain growth in the solid state .
1- solidification from the melt :
Czochralski method :
A seed crystal is gradually withdrawn vertically from the surface of a molten metal leads to building a crystal rod with an orientation to the seed and the crystals produced are irregular in the cross section and this result in no contact with the mould , so contamination is reduced. This technique is used to produce germanium and silicon crystals for transistors . It's very useful for silicon which is very reactive at the melting point 1412 degree centigrade .
The crystal rod is rotated to ensure uniform cross section and to get homogeneity in the dispersion of the alloying elements. The orientation of the resulting crystal is controlled by a seed crystal of the required orientation .
In the Bridgeman method , the metal content is lowered through a vertical furnace with a temperature gradient and the crystal is nucleated at the end and grows upward in the content . the metal content i.e. the mould made from pure graphite when using factory metals such as Aluminum , copper , silver , nickel. .But low melting point metals such as tin ,zinc and cadmium are grown up in heat resisting glass tubes . Metals which react with carbon alumina is used .figure 2 Bridgeman furnace .
Single crystals can be produced in horizontal furnaces and the mould is graphite .
Another method is the application of the zone melting technique where a molten zone is moved from one end of the bar to another which is also a method of purification .
Crystals can also be produced vertically by the floating zone method in which the metal is not in contact with a container using cold grips to hold the specimen and a molten zone is produced by high frequency heating or electron bombarding from a filament in a high purity argon atmosphere or good vacuum the length of the zone being proportional to the square root of the surface tension to the square root of the density of the metal this method is used in high melting point metals like tungsten, tantalum , molybdenum ,vanadium , nickel , rhenium , etc.
Grain growth in the solid state:
The most widely used method is the strain-anneal technique.
A fine grained annealed specimen is is strained by 1- 2 percent in tension then annealed at a gradually increasing temperature. Nucleation and growth of a few and often one grain and this grain absorb all strains during annealing . In this way single crystal rods of aluminum and some of its alloys can be grown up to 50 cm long by a temperature gradient 20 degree per one cm for pure aluminum and for some aluminum alloys 1000 degree per cm . Most metals which has phase transformation producing single crystal by slow cooling through the transformation like iron , titanium , uranium and zirconium .
See